Describe the Physiological Mechanisms of Medication Action
For example if you are assigned Calcium Channel Blockers explain the role of calcium channels in muscle contraction. There is overwhelming evidence pointing to the inhibition of cyclooxygenase enzyme as the main mechanism of NSAIDs analgesic antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties.

Lamotrigine Pharmacological Mechanism Of Action Clinical Application
Actions of Drugs on the Body.

. Patient was educated on Carvedilol and its mechanism of action as follows. Describe the physiological mechanisms of medication action We like to provide great site with complete features what you want to implement in your business. Pharmacopoeia gives the guidelines and ranges.
Carvedilol is a nonselective Beta blocker drug that inhibits the action of catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline on both the Beta-1 and Beta-2 receptors. Several mechanisms that in vivo appear to influence the number of functional receptors within a responsive cell have been defined. In other words it can be said that certain neurophysiological mechanisms are responsible for particular.
Its pharmacologic mechanisms of action are different from other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Since the characterization of this mechanism by Vane for aspirin 10 other drugs in this class have proven consistent this mechanism. Main types of drug targets and their mechanisms of action.
The decision lies with the doctor. The atropine results in modifications of the heart rate. For example behavior of an animal including human beings is one of the functional outcomes of the brain.
In order to understand how a medication works you need to understand the normal physiological processes. Most drugs act by altering the various body control systems which may be receptors enzymes or ion channels. It considers both drug action which refers to the initial consequence of a drug-receptor interaction and drug effect which refers to the subsequent effects.
Coupled directly to an ion channel. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targets to which the drug binds such as an enzyme or receptor. All factors affecting absorption and biotransformation may influence the outcomes of drug actions.
Interaction with other drugs. Mechanism of Action Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Chapter 32 Medication Administration Flashcards Quizlet Cyclooxygenase is required to convert arachidonic acid into thromboxanes prostaglandins and prostacyclins.
Briefly describe the mechanism of action physiological role of the medication. Inhibition of Beta-1 receptors results in slowing of heart rate and decreases the force of contraction of heart muscle. From the examples select one acid one base and one salt and describe specifically how and where they are used in therapeutic processes.
Inhibit GABA transporter and reduce neuronal GABA reuptake. In pharmacology the term mechanism of action refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. These channels are known as ligand-gated because it is receptor binding that operates them in contrast to voltage-gated.
These are autoregulation of receptor synthesis modulation of receptor phosphorylation and regulation of receptor levels by factors that mediate other signal transduction pathways. State and explain the type and class of medication. INTRODUCTION Mechanism of drug actionpharmacodynamics Study of drug effects Modification of one drugs action by another 6.
Receptor sites have specific affinities for drugs based on the chemical. Mist can become a Blog an Agency a Hospital a Sports a a Portfolio a Spa a Restaurant a University a Corporate website an E-Store a Construction Business a Hosting Company an. Activation opens the channel making a cell membrane permeable to specific ions.
Chloride ions into the cell and hyperpolarizes the neuron. These various mechanisms include. The breadth and depth of the studies in this topic illustrate the complex actions of alcohol and drugs of abuse on various neurobiological systems.
There exists no specific dose. Giving optimum dose is mandatory for desired results. Discuss the mechanism of action for each of the drugs.
Pharmacodynamics is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action on the body or on microorganisms and other parasites within or on the body. Up to 10 cash back The mechanisms by which the organ systems of the body function are often referred to as physiological mechanisms. Drugs that inhibit Calcium channels.
Atropine Mechanism of Action 1. Actions of drugs are. By inhibition of mitochondrial respiration but also perhaps by inhibition of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and a mechanism involving the lysosome.
Act on GABA receptor. Limit activation of voltage activated Ca channel. Its pharmacologic mechanisms of action are different from other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents.
Metformin has been shown to act via both AMP-activated protein kinase AMPK-dependent and AMPK-independent mechanisms. PRINCIPLES OF DRUG ACTION Alter the pace of ongoing activity not impart new function Types of drug action. Together this work represents the most current understanding of how acute andor chronic exposure to abused substances engages andor pathologically alters distinct brain circuits.
In low doses a slight slowing of the heart is attributed to the incidental parasympathetic effect and central vagal stimulation that leads to a short term increase of acetylcholine.

Lamotrigine Pharmacological Mechanism Of Action Clinical Application
What Is The Mechanism Action Of Aspirin When Being Used As An Antipyretic Quora

What Is The Mechansim Of Action Of Methylphenidate

Calcium Channel Blockers Mechanism Of Action Google Search Calcium Channel Blockers Pharmacology Channel

Safety Efficacy And Mechanisms Of Action Of Cannabinoids In Neurological Disorders The Lancet Neurology
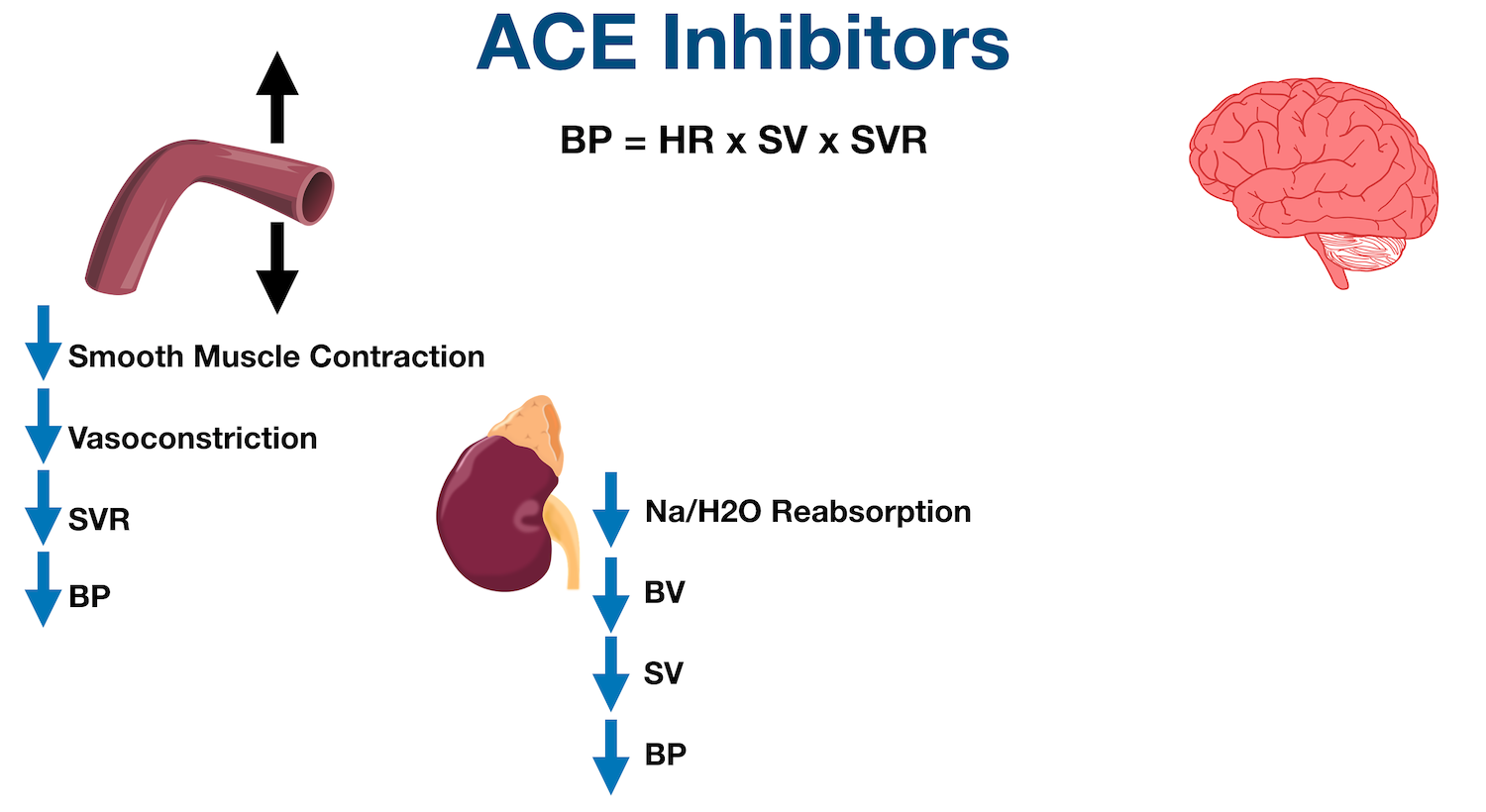
Ace Inhibitors Drug List Side Effects Mechanism Of Action Example Medications Contraindications Ezmed

Drug Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
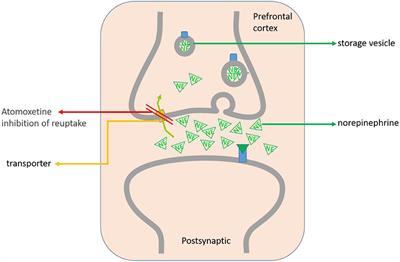
Frontiers The Mechanism Clinical Efficacy Safety And Dosage Regimen Of Atomoxetine For Adhd Therapy In Children A Narrative Review Psychiatry
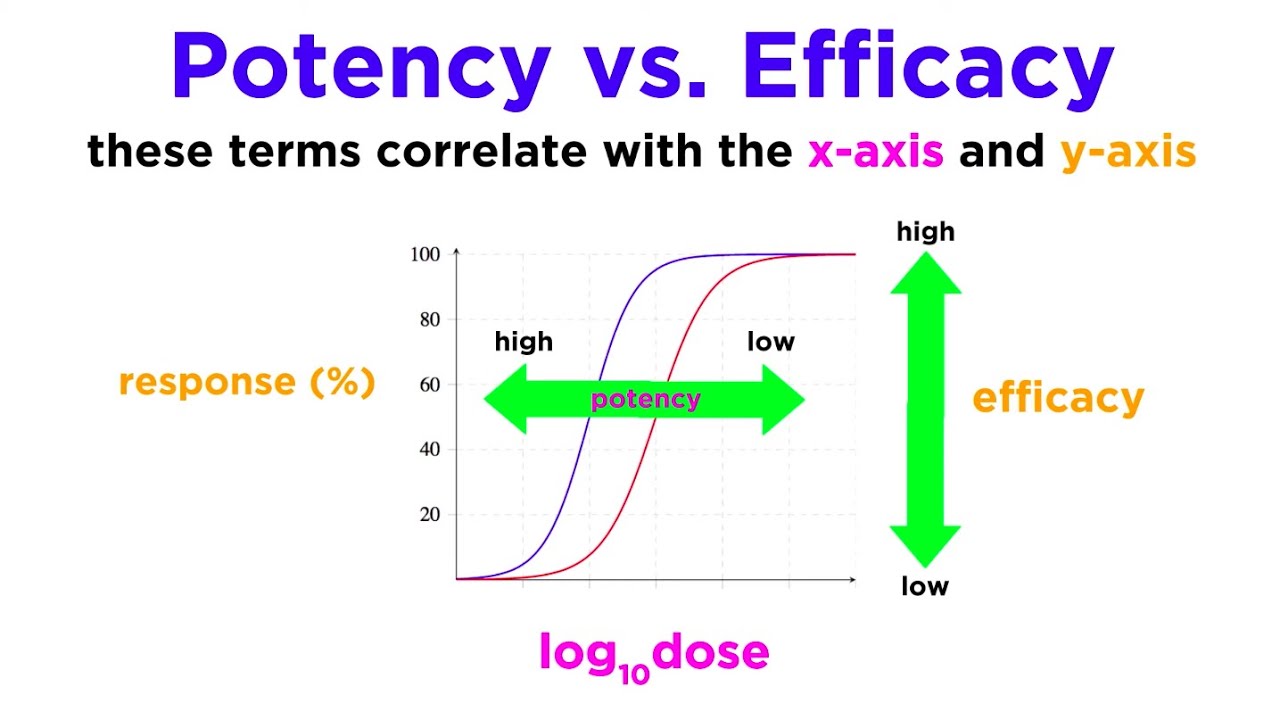
Pharmacodynamics Mechanisms Of Drug Action Youtube

A Focus On Vortioxetine Mechanism Of Action And Efficacy

Antihypertensive Medications Site And Mechanism Of Action Of The Various Antihypertensive Drugs Pharmacology Nursing Pharmacology Nursing Classes
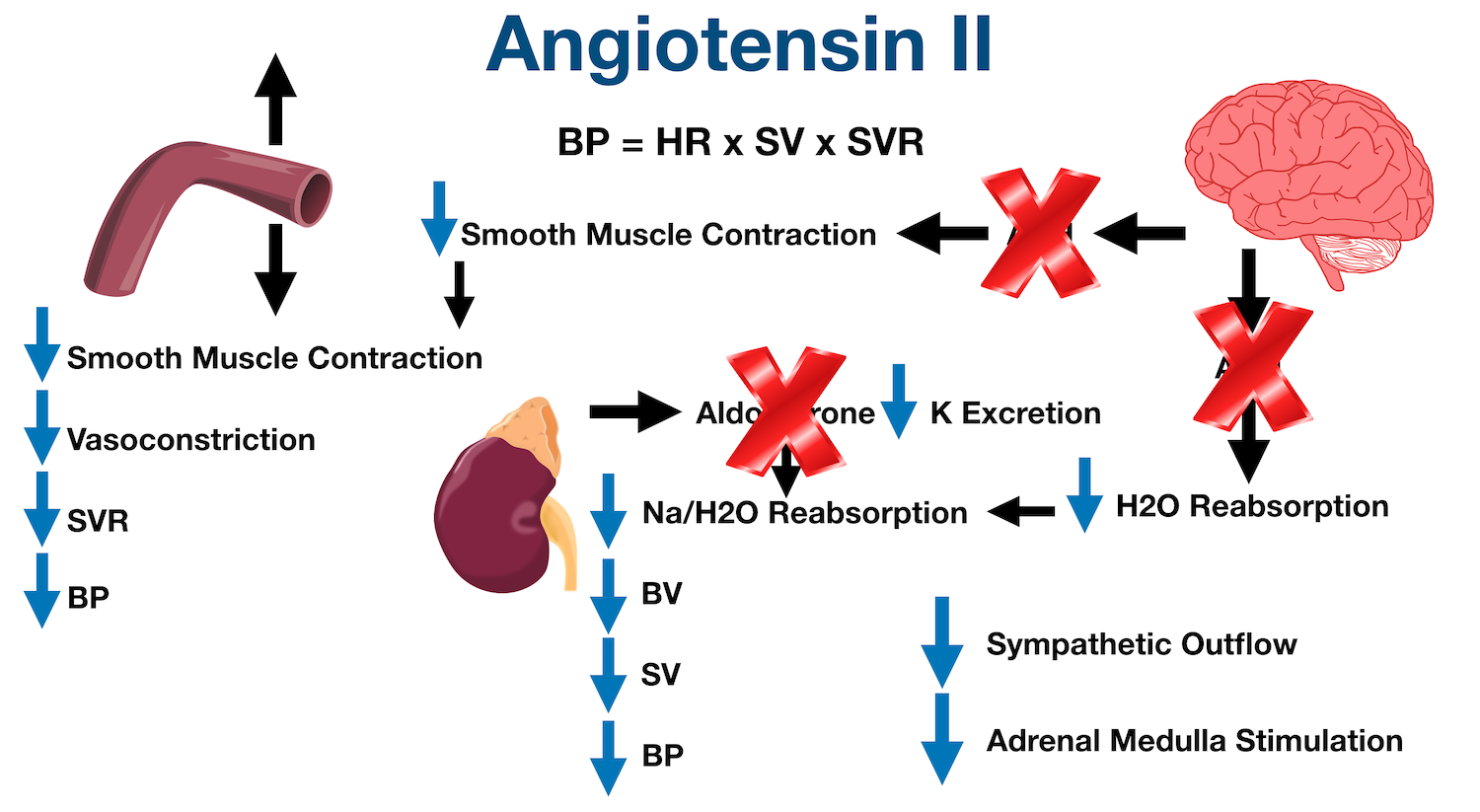
Ace Inhibitors Drug List Side Effects Mechanism Of Action Example Medications Contraindications Ezmed
Mechanisms Of Drug Action And Resistance

Nitroglycerin Mechanism Of Action For Angina Pectoris Youtube

Mechanism Of Action Of Antipsychotic Agents Psychopharmacology Institute

Cv Pharmacology Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Ace Inhibitors

Angiotensin Ii Receptor Blockers Arbs Indications Side Effects Mechanism Of Action Examples Ezmed

Comments
Post a Comment